Habilitation for HITSter Rüdiger Pakmor
The astrophysicist Dr. Rüdiger Pakmor from the Theoretical Astrophysis group (TAP) successfully completed the habilitation process at Heidelberg University. At …

EuroNeurotrophin project starts
14 Early Stage Researchers to be trained in a European training network for the discovery of small molecule neurotrophin mimetics as candidate …

CBI Junior Group: Mission Accomplished
HITS Junior Group “Computational Biology” is bringing its work to a close with two publications in “Nature.” According to Group Leader …

How black holes shape the cosmos
Astrophysicists from Heidelberg, Garching, and the USA gained new insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies. They calculated how black …

The largest genome ever: Decoding the Axolotl
A team of researchers led by scientists in Vienna, Dresden and Heidelberg has decoded the entire genetic information of the Mexican …
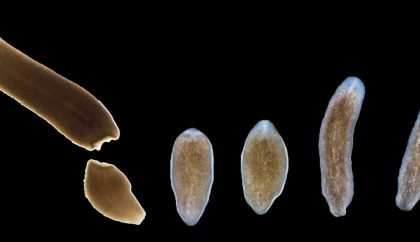
A new genome for regeneration research
The planarian flatworm Schmidtea mediterranea is an extraordinary animal. Even when cut into tiny pieces, each piece can regenerate back into …
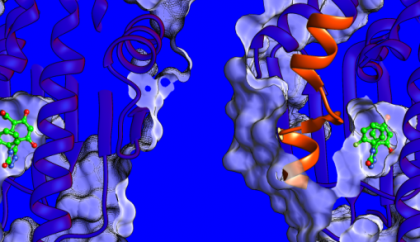
A matter of mobility: multidisciplinary paper suggests new strategy for drug discovery
A joint industry/academia study of a cancer target protein reveals unusual relation between binding site flexibility and drug-target lifetime. The …

Kerstin Hoppenhaus and Andreas von Bubnoff to be “Journalists in Residence” at HITS
The Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies gives science journalists the opportunity to deepen their knowledge of computer-based, data-driven science with a …

Library of galaxy histories reconstructed from motions of stars
The CALIFA survey allows to map the orbits of the stars of a sample of 300 galaxies, a fundamental information to know …
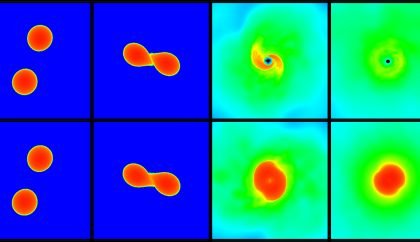
Neutron Stars on the Brink of Collapse
Neutron stars are the densest objects in the Universe; however, their exact characteristics remain unknown. Using simulations based on recent observations, …
