- This event has passed.
Colloquium Erin R. Johnson: Dispersion Interactions in Density-Functional Theory and Application to Molecular Crystal-Structure Prediction
Online Colloquium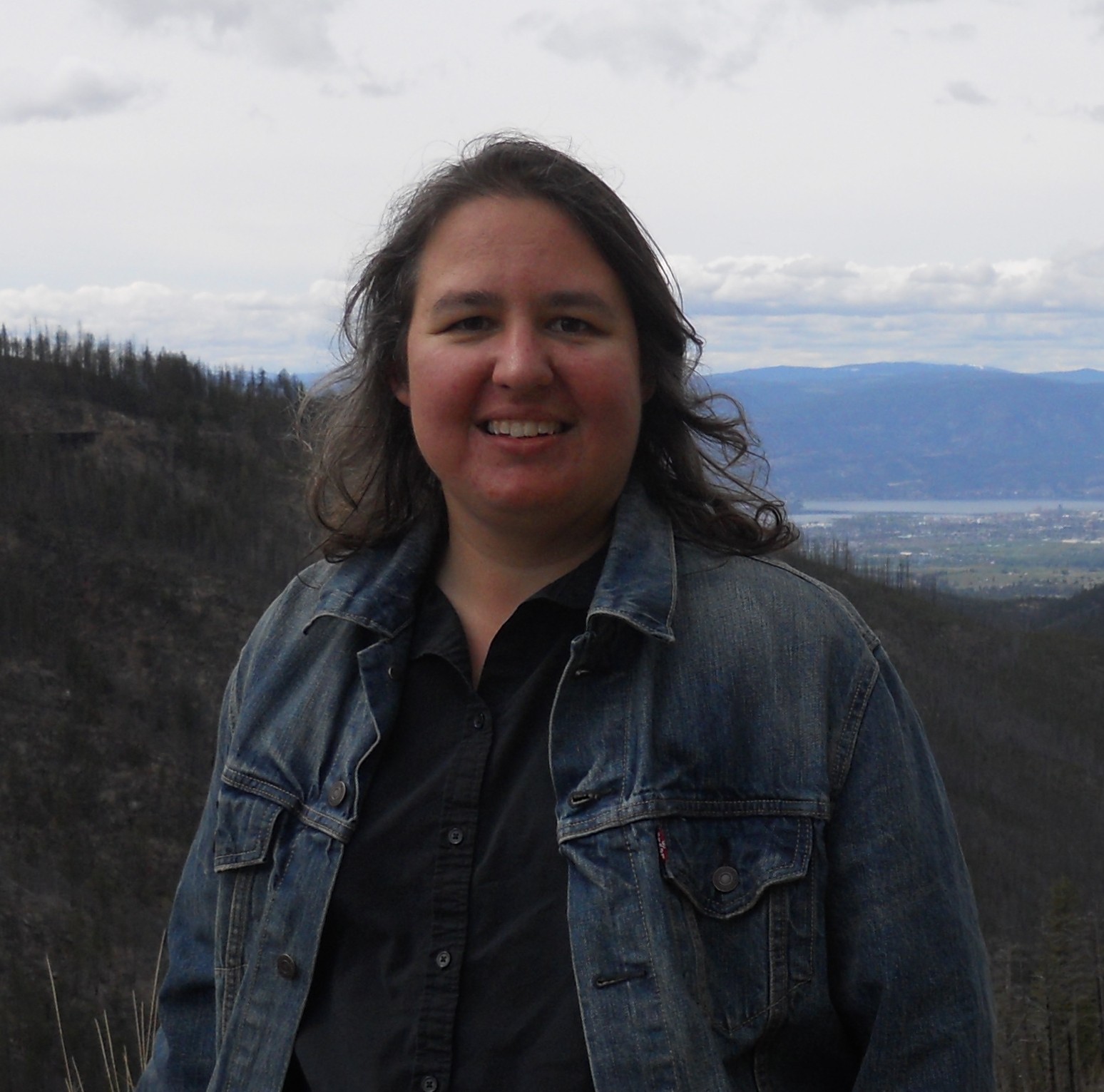
By Erin R. Johnson, Department of Chemistry, Department of Physics & Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada
The exchange-hole dipole moment (XDM) method is a density-functional model of London dispersion based upon second-order perturbation theory. The XDM dispersion coefficients are non-empirical and depend directly on the electron density and related properties, allowing variation of the atomic dispersion coefficients with changing chemical environment. XDM offers simultaneous high accuracy for a diverse range of chemical systems, including layered materials and metal surfaces. In this talk, recent applications of XDM will be presented, with a focus on molecular crystal-structure prediction (CSP). We will illustrate the utility of composite methods for CSP of chiral helicenes, which have applications in organic electronics, and of several pharmaceutical compounds. Finally, the effect of the density-functional delocalisation error on CSP is highlighted for organic acid-base co-crystals.
Curriculum vitae:
Please see: CV-short
REGISTRATION: